Asset Publisher
Asset Publisher
Polish hit
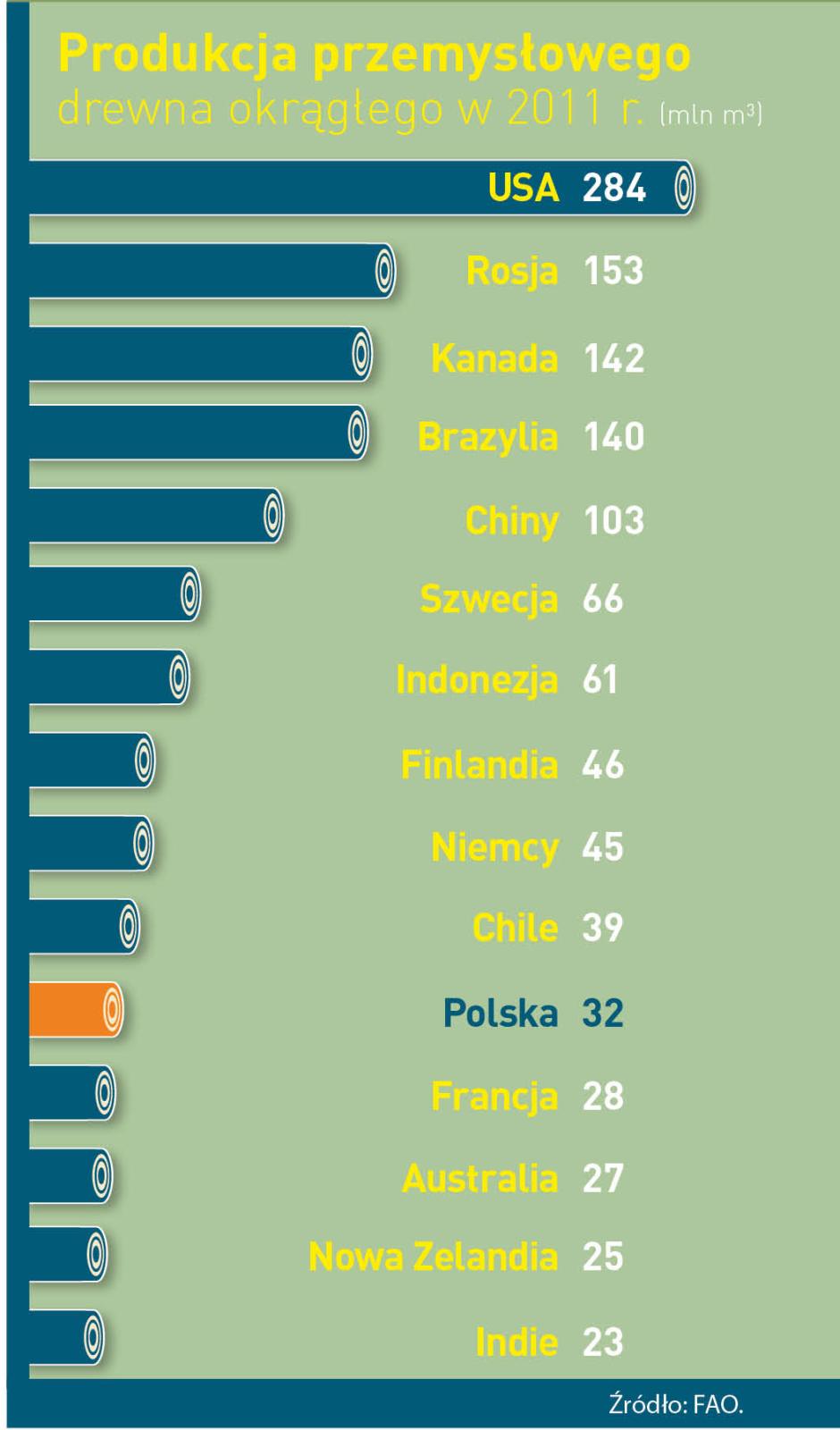
Polish products made of wood – furniture, window and door frames, yachts or paper and packages – these are real hits of the market.
Our country is the is the 10 largest producer of furniture and the 4 largest furniture exporter in the world. Wood industry sells abroad goods of its approximate value of 45 million zl annually, what constitutes 10 % of the whole Polish export. The measurement of the essential role of forestry and timber based sector in our management is that, it works out about 2 % of GDP (Gross Domestic Product). Not only it gives work to thousands of people, but it is also an engine of investment and of development of innovative technologies. From the beginning of transformation, it drew foreign capital of its value over 30 million zl.
Forest gives work
The State Forests belong to the leading group of employers in Poland. However, both forest and timber provide for workers with several thousand of Forestry Services Companies, which within the contract of mandate deal with, among others, planting trees and their nursing, wood logging and its transportation. And above all cooperate with people employed in several dozen thousand of companies creating wood and furniture industry and paper manufacture. Summing up, it gives as many as 375 thousand of Poles altogether. Statistically, every hundred inhabitant of our country works in the sector connected with forestry and wood processing.
Among private companies of forestry and timber based sector, there are also big companies with the share of foreign capital , and big and medium sized indigenous companies, but 9 of 10 companies in this sector are small plants employing less than 10 people. These are often family companies, cultivating multigenerational traditions connected with forestry and working in less developed regions of the country. There, forestry and wood industry, as well as agriculture constitute the basis of maintaining hundred thousand of families. As many as 600 % of all working places in the forest and wood based sector are located within rural areas.
Forest and wood based sector works out about 2 % of Polish GDP (Gross Domestic Product).
- 2 % of Polish GDP works out forest and wood based sector .
- Poland takes 4 place as the largest furniture exporter and 10 place as the largest producer of furniture.
- 50 % of paper and 9 of 10 pieces of furniture produced in Poland is exported abroad
- The value of annual export of Polish goods of wood and furniture industry and paper manufacture equals 45 billion zl (it is 10 % of the whole export).
- 30 billion zl , as direct foreign investments, have been drown since 1990 by Polish wood based sector (5,5 % of all).
- 100 kg of paper is used annually by statistic Pole (an average of UE is 160 kg, for USA – 230 kg).
Source: E. Ratajczak „Potencjał gospodarczy przemysłów opartych na drewnie i perspektywy ich rozwoju (Economic performance of wood – based industries and perspectives of their development)", GUS, Warszawa 2012.
 Asset Publisher
Asset Publisher
 Asset Publisher
Asset Publisher
Rezerwat Mójka
Rezerwat Mójka
Rezerwat został utworzony dnia 25 lipca 1997 roku na powierzchni 288,80 ha w leśnictwie Kąkolówka (oddz. 81-89) w celu zachowania ze względów naukowych, dydaktycznych i krajobrazowych kompleksów lasu bukowo-jodłowego oraz osiedlonego w zbiorowiskach wodno-błotnych bobra.
Rezerwat leży w granicach Hyżnieńsko-Gwoźnickiego OChK. Do najcenniejszych elementów przyrody rezerwatu, stanowiących główny przedmiot ochrony, należą ekosystemy leśne tworzone przez lasy jodłowe ze znacznym udziałem buka.
Na uwagę zasługuje obecność wilgotnego podzespołu żyznej buczyny karpackiej z czosnkiem niedźwiedzim, kwaśnej buczyny górskiej a także nadrzecznej olszyny górskiej.
Cenną fitocenozą jest również grąd subkontynentalny. Bogactwo florystyczne wyraża się obecnością 340 gatunków roślin naczyniowych, w tym 24 chronionych ( 18 objętych ochroną ścisłą). Na uwagę zasługuje wśród nich: listera jajowata, storczyk szerokolistny i plamisty, podkolan biały, cebulica dwulistna, podrzeń żebrowiec, widłaki: goździsty, jałowcowaty i wroniec, kłokoczka południowa i zimowit jesienny. Za szczególną osobliwość florystyczną rezerwatu należy uznać rosnący tu w znacznym skupieniu czosnek niedźwiedzi.
W drzewostanach rezerwatu występują okazałe, wiekowe egzemplarze drzew spełniających kryteria pomników przyrody, z których na szczególną uwagę zasługuje buk o oddz. 86b, osiągający obwód 310 cm. Interesująca jest fauna omawianego obiektu na czele z bobrem europejskim, z pozostałych gatunków należy wymienić: dzięcioła trójpalczastego, salamandrę plamistą. Na terenie rezerwatu pojawia się również bocian czarny. W rezerwacie można odnaleźć kilka interesujących elementów przyrody nieożywionej, np. w południowo-wschodniej jego części znajduje się interesujący kamień będący pomnikiem przyrody.
Na granicy oddziałów 84h oraz 87a, w dolinie potoku, znajduje się rumowisko skalne z naniesionych przez potok różnej wielkości głazów i kamieni. Na potoku występują niewielkie, ale dość liczne wodospady.
Przez teren rezerwatu prowadzi ścieżka przyrodniczo - edukacyjna. Utworzona wspólnym wysiłkiem Gminy Błażowa i Nadleśnictwa Strzyżów.